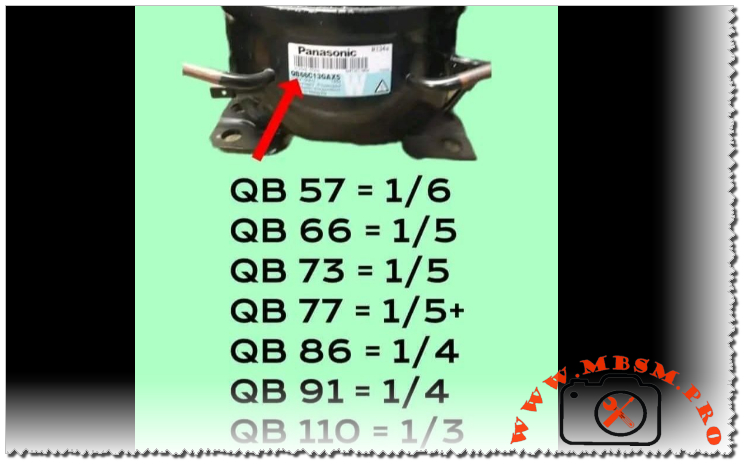
Panasonic QB110C25CAX0 1/3 HP Compressor Specifications and Replacement

Mbsmpro.com, Compressor, QB110C25CAX0, 1/3 hp, Panasonic, R134a, 220V, LBP, Refrigerator, Freezer
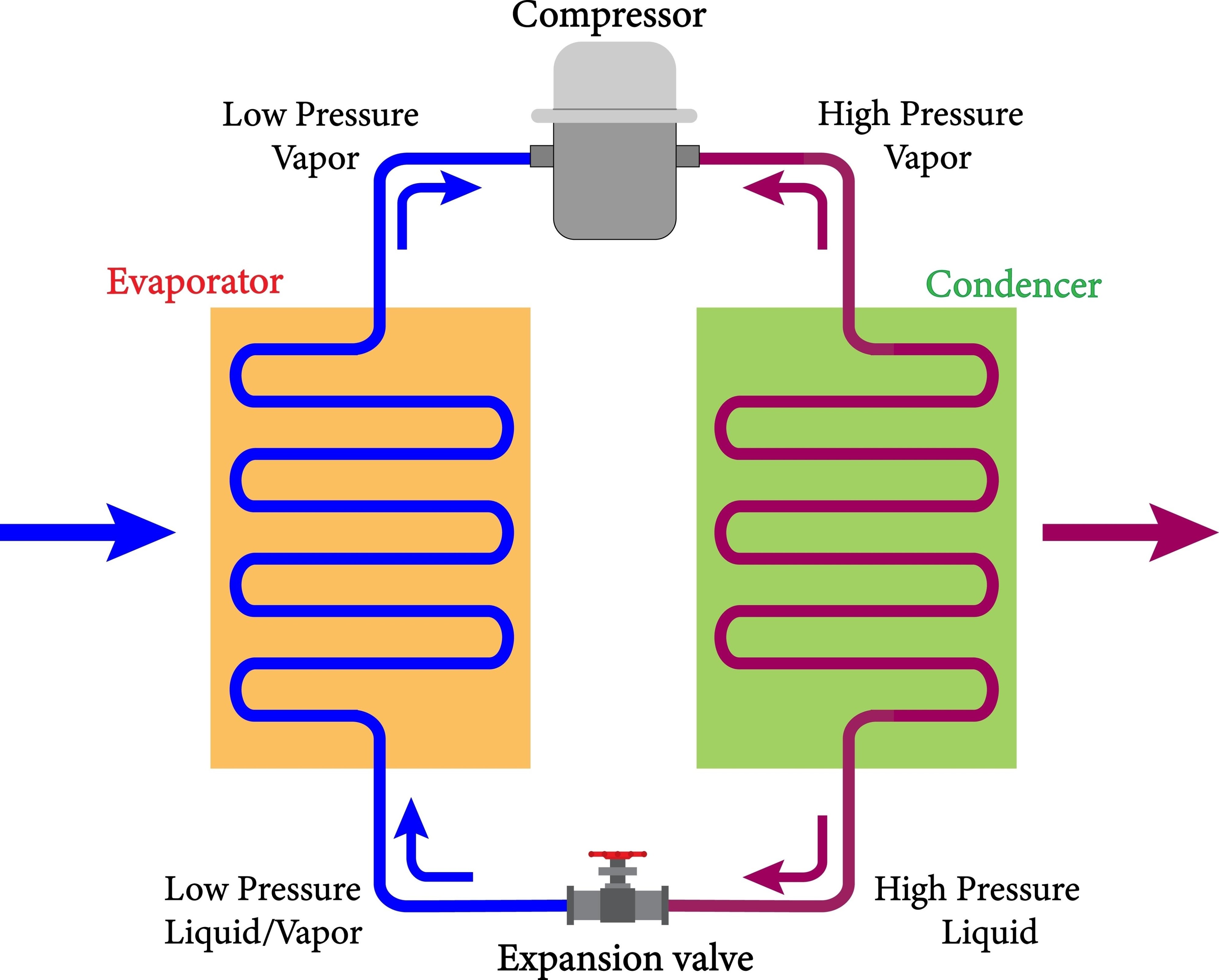
The Panasonic QB110C25CAX0 stands as a heavyweight in the world of domestic and light commercial refrigeration. Specifically engineered for Low Back Pressure (LBP) applications, this reciprocating compressor is the heart of many high-capacity household refrigerators and deep freezers. Operating on R134a refrigerant, it balances environmental standards with the robust cooling performance required for tropical climates.
The “QB” series by Panasonic is renowned for its durability. With a displacement of 11.0 cm³, this model provides the necessary “punch” to pull down temperatures quickly in units ranging from 400 to 600 liters. Its design focuses on thermal protection and energy efficiency, ensuring that the motor remains cool even during extended run cycles in demanding environments.
Technical Specifications and Performance Data
| Feature | Specification |
| Model | QB110C25CAX0 |
| Utilization | LBP (Low Back Pressure) |
| Application Domain | Freezing / Cooling |
| Cooling Wattage (-23.3°C) | 280 W |
| Cubic Feet Capacity | 18 – 22 cu.ft |
| Liters Capacity | 500 – 620 L |
| Cooling Capacity (Kcal/h) | 241 Kcal/h |
| Oil Type & Quantity | POE or Mineral (250ml – 280ml) |
| Horsepower (HP) | 1/3 HP |
| Refrigerant Type | R134a |
| Power Supply | 220V-240V / 50-60Hz / 1PH |
| Cooling Capacity (BTU/h) | 955 BTU/h |
| Motor Type | RSIR (Resistive Start-Inductive Run) |
| Displacement | 11.0 cm³ |
| Winding Material | Copper |
| Amperage (RLA) | 1.4 A – 1.6 A |
| LRA (Locked Rotor Amps) | 12.0 A |
| Relay Type | PTC / Electromagnetic |
| Capacitor | Generally not required (RSIR), optional for CSIR |
| Fan Requirement | Static cooling (Natural) / Fan cooling recommended for tropics |
| Commercial Status | Semi-Commercial / Heavy Domestic |
| Country of Origin | Malaysia |
Efficiency Metrics (COP) & Performance Curve
| Evaporating Temp (°C) | Cooling Capacity (Watts) | Power Consumption (Watts) | COP (W/W) |
| -30 | 185 | 170 | 1.09 |
| -25 | 255 | 195 | 1.31 |
| -23.3 (Standard) | 280 | 205 | 1.37 |
| -20 | 340 | 225 | 1.51 |
| -15 | 445 | 250 | 1.78 |
| -10 | 570 | 280 | 2.04 |
Replacement Cross-Reference
1. Same Refrigerant (R134a) – 1/3 HP Substitutes
- Embraco: FFI10HBX or FG100HAK
- Secop (Danfoss): TLES10KK.3
- Tecumseh: AE1390Y / AE4440Y
- LG: MA110LBJG
- Jiaxipera: N1114GZ
2. Alternative Refrigerant (R600a/R12/R22 Conversions)
- Embraco (R600a): VEMZ 9C (Inverter tech required)
- Panasonic (R600a): QB110G Series (Check displacement compatibility)
- Secop (R600a): BD110F
- Tecumseh (R12 Old): AE1390AS (Requires system flush)
- Samsung (R134a): MK190C-L2U
Engineering Insight: Why Choose the QB110?
When comparing the QB110 (1/3 HP) to its smaller sibling, the QB77 (1/5+ HP), the difference in volumetric efficiency is striking. While the QB77 is perfect for standard kitchen fridges, the QB110 is designed for “chest” freezers or large side-by-side units.
Pro Tip for Technicians:
Always ensure the capillary tube is sized correctly for a 1/3 HP load. For an LBP R134a setup with this compressor, a capillary of 0.036 ID is generally the starting point. Using a 1/5 HP capillary on this motor will cause high head pressure and premature compressor failure.
Maintenance Notice: Since this is an R134a system, moisture is your greatest enemy. Always replace the filter drier and pull a vacuum below 500 microns before charging.
Focus Keyphrase: Panasonic QB110C25CAX0 1/3 HP Compressor Specifications and Replacement
SEO Title: Mbsmpro.com | Panasonic QB110C25CAX0 Compressor | 1/3 HP R134a LBP Review
Meta Description: Discover the full technical specifications of the Panasonic QB110C25CAX0 1/3 HP compressor. Includes cooling capacity, COP tables, wiring details, and a comprehensive replacement guide for R134a refrigeration systems.
Slug: panasonic-qb110c25cax0-1-3-hp-compressor-specs
Tags: Mbsmgroup, Mbsm.pro, mbsmpro.com, mbsm, Panasonic, QB110C25CAX0, 1/3 HP Compressor, R134a, LBP, Refrigeration Parts, Embraco FFI10HBX, Secop TLES10KK, LG MA110, Compressor Cross Reference.
Excerpt: The Panasonic QB110C25CAX0 is a high-performance 1/3 HP reciprocating compressor designed for Low Back Pressure (LBP) applications. Operating on R134a refrigerant, it delivers 280W of cooling capacity at -23.3°C, making it ideal for large domestic freezers and commercial coolers. This guide provides technical data, COP efficiency tables, and compatible replacement models for technicians.