White Whale WR‑5395 HBX, 540L

White Whale 540L Black No Frost Refrigerator with Water Dispenser – Full Technical Look with Compressor Power
Reference model and compressor power
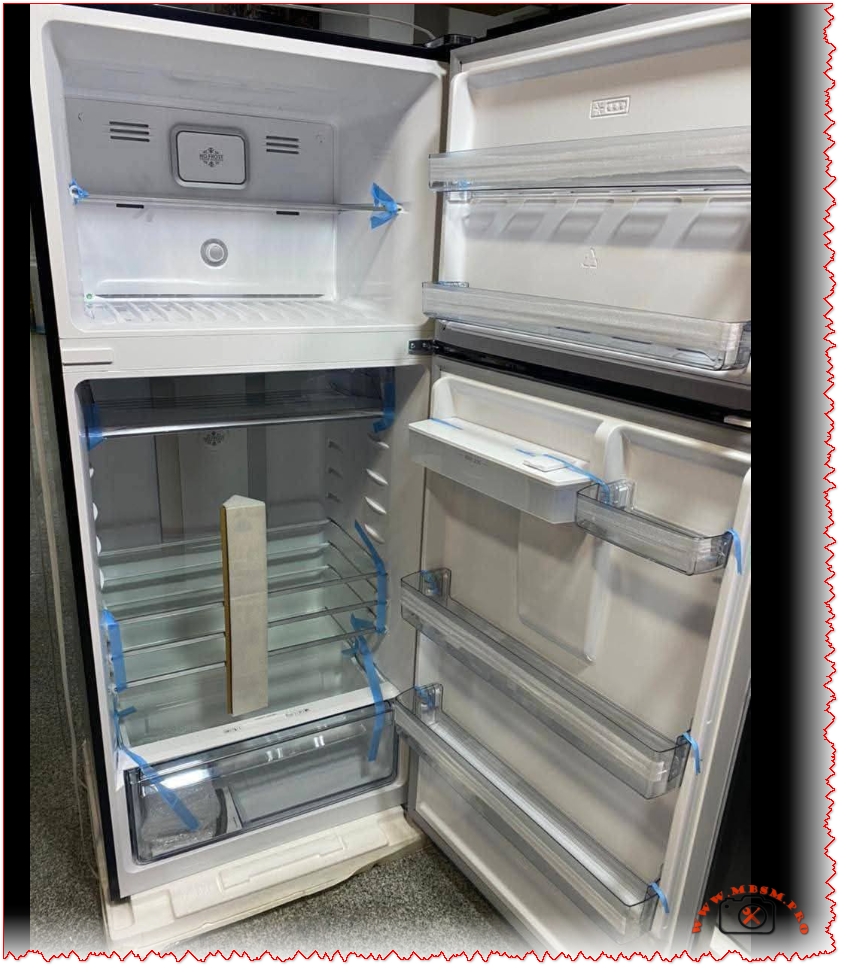
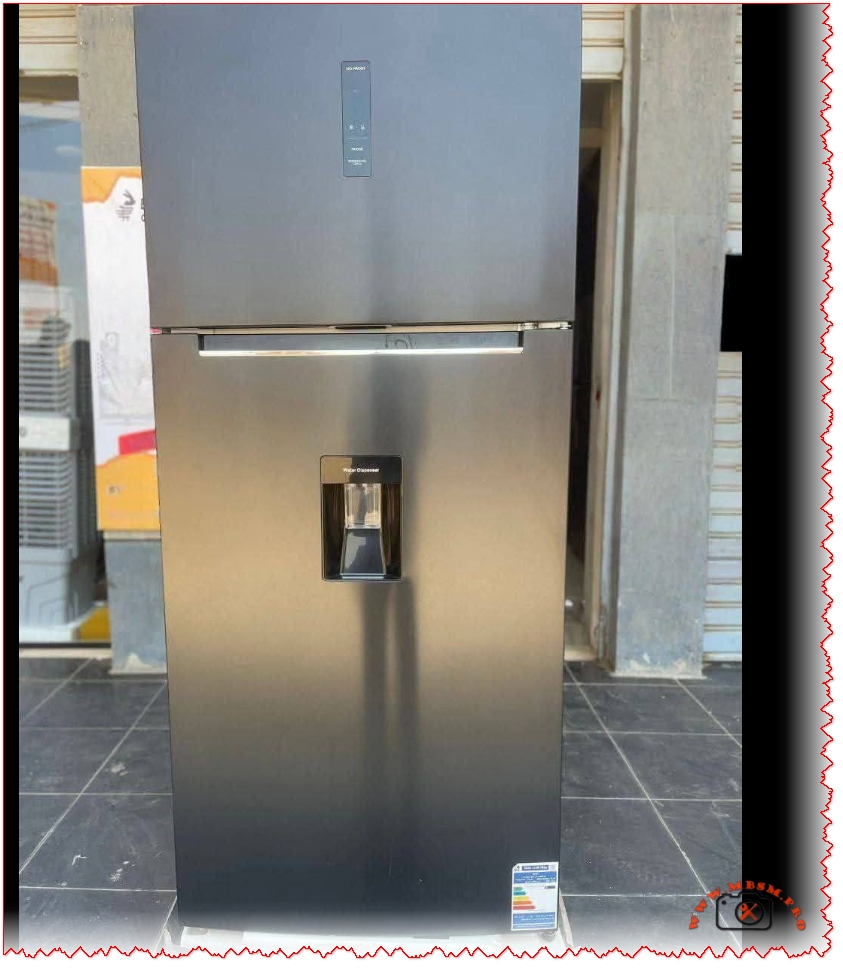
The refrigerator in your photos corresponds to the top‑mount White Whale WR‑5395 HBX: a 540‑liter, black, No Frost, 2‑door model with water dispenser and inverter compressor.
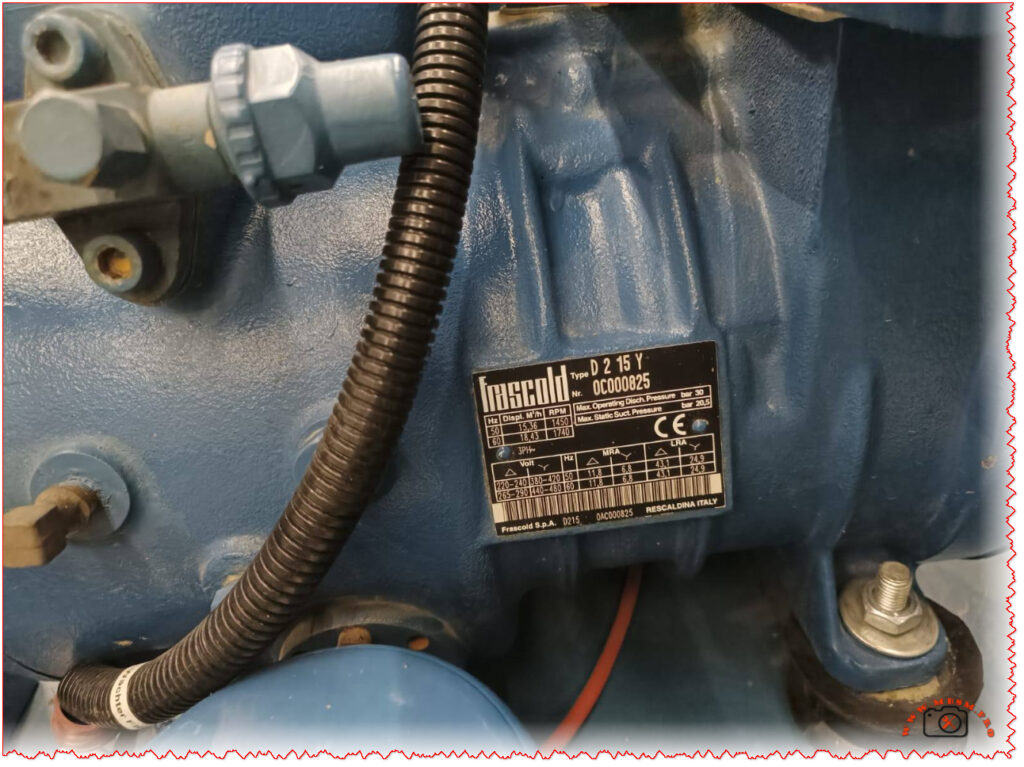
Official and retailer specification pages list the capacity, dimensions, features, and inverter motor, but they do not publish compressor horsepower (HP) or input wattage (W) for this model; only general “energy‑saving inverter motor” information is provided.
From similar 540L top‑mount inverter refrigerators, the compressor input is typically in the 180–260 W range, which corresponds to approximately 1/4 to 1/3 HP in residential R600a systems, but this is an engineering estimate, not an official White Whale figure.
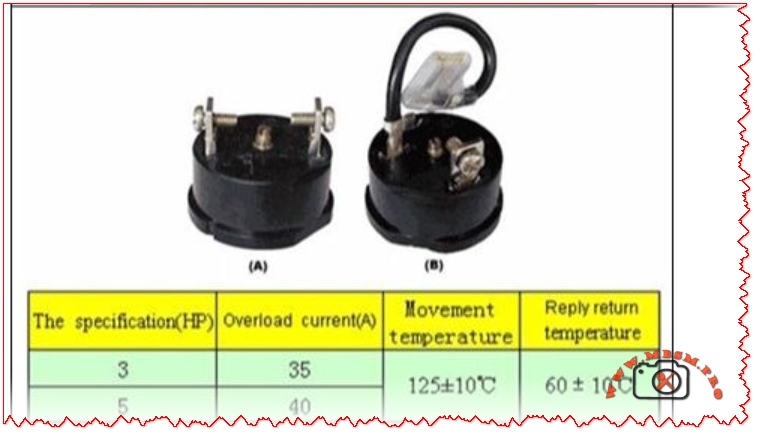
For an exact HP or watt rating you would need either the compressor nameplate (inside or on the back of the unit) or a factory data sheet from White Whale’s technical support, because public catalogues for WR‑5395 HBX only state “inverter compressor / energy‑saving motor” without power numbers.
Updated article with explicit reference
White Whale 540L Black No Frost Refrigerator WR‑5395 HBX with Inverter Compressor and Water Dispenser
The White Whale WR‑5395 HBX is a 540‑liter black top‑mount refrigerator aimed at families who need generous storage, efficient cooling, and a modern look in one appliance.
It combines a full No Frost system, inverter compressor, digital control and a built‑in water dispenser, making it one of the most attractive options in White Whale’s large‑capacity range.
Design and layout
- Sleek black or black‑glass door finish with a slim horizontal handle and integrated dispenser on the refrigerator door.
- Inside, the cabinet offers adjustable tempered‑glass shelves, large vegetable drawer, multiple door balconies and bright LED interior lighting for clear visibility.
Cooling system and compressor
- The WR‑5395 HBX uses a No Frost, multi‑airflow cooling system that keeps a stable temperature and prevents ice build‑up in both freezer and fridge compartments.
- An inverter compressor modulates its speed according to cooling demand, cutting energy consumption and noise while maintaining fast pull‑down and a quick‑freeze mode in the top freezer.
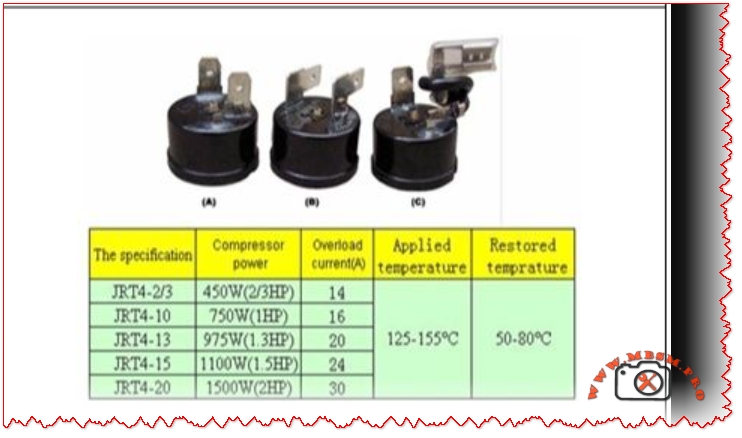
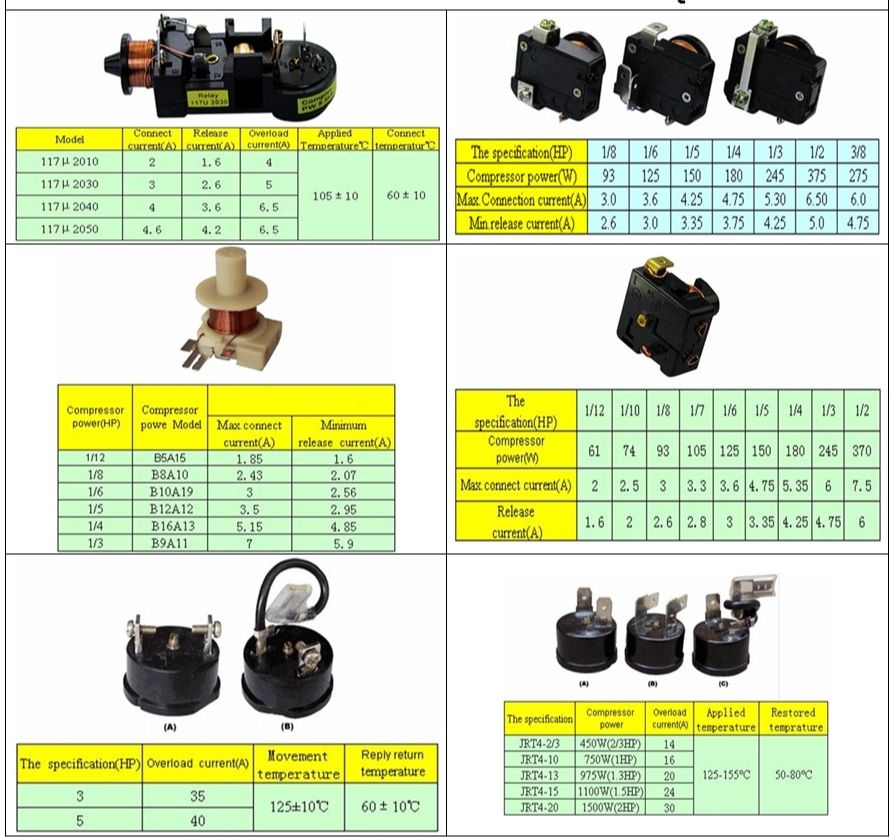
- Public datasheets do not disclose the exact compressor HP or watt input, but White Whale and retailer pages only describe it as an “energy‑saving inverter motor” without numeric power ratings.
Typical power range (engineering estimate)
- Comparable 540L, No Frost, inverter top‑mount refrigerators with R600a usually run compressors rated between 180 W and 260 W, which equates to roughly 1/4–1/3 HP under nominal conditions.
- This range is offered as a technical approximation based on similar‑size inverter models; for installation, warranty or spare‑part selection, always rely on the actual compressor label or an official White Whale technical sheet for WR‑5395 HBX.
Main technical specifications
Practical buying notes
This refrigerator suits users who want a large, family‑size fridge with No Frost convenience, inverter efficiency and a black, contemporary finish.
If you need exact compressor HP or wattage—for example, to size an inverter, voltage stabiliser or replacement compressor—check the compressor nameplate on the back of the unit or request a detailed technical datasheet from White Whale service using the WR‑5395 HBX model code.