Donper L65CZ1 Compressor Specs and Replacements

R134a, refrigerant, compressor L65CZ1, 220-240V 50Hz, LBP, 1/5 hp
Description
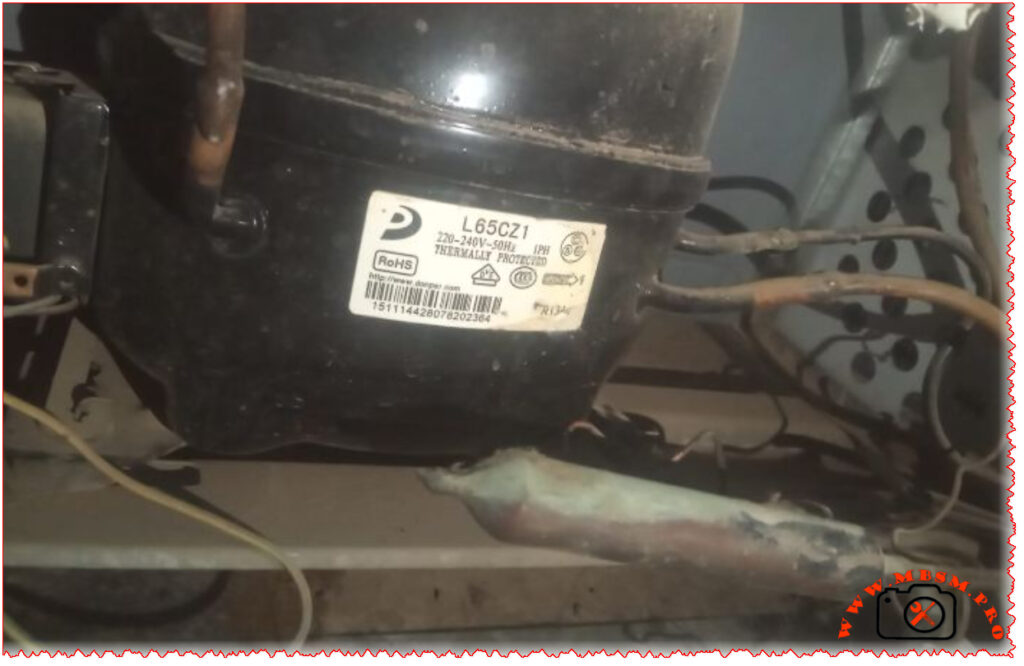
Mbsm.pro: Compressor, Donper, L65CZ1, 1/5 HP, 1Ph, 220-240V 50Hz, R134a, LBP, Refrigeration & Freezing
Technical Specifications Table
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Model | L65CZ1 |
| Manufacturer | Donper (Dongbei Compressor) |
| Utilisation | LBP (Low Back Pressure) |
| Domaine | Domestic Refrigerators / Freezers / Wine Coolers |
| Cooling Wattage at -23.3°C | 158-170 W (ASHRAE) |
| Cubic Feet Capacity | 5 to 10 cu. ft. (Depending on insulation) |
| Litres Capacity | 150 to 280 Liters |
| Kcal/h | 136 Kcal/h |
| TON | ~0.045 Tons |
| Oil Type and Quantity | POE (Polyolester) or Mineral Oil, 280-320 ml |
| Horsepower (HP) | 1/5 HP |
| Refrigerant Type | R134a |
| Power Supply | 220-240V / 50Hz / 1Ph |
| Cooling Capacity BTU | 464 BTU/h |
| Motor Type | RSIR (Resistance Start Induction Run) |
| Displacement | 6.5 cm³ |
| Winding Material | Copper |
| Pression Charge | 8-12 Bar (High Side) |
| Capillary Recommendation | 0.028″ or 0.031″ (Length varies by application) |
| Compatible Appliances | Domestic refrigerators, freezers, wine coolers, beverage coolers |
| Temperature Function | -25°C to +10°C |
| With Fan or No | Yes (Fan cooling required for compressor) |
| Commercial or No | Domestic/Light Commercial Grade |
| Amperage (FLA) | 1.2 A to 1.5 A |
| LRA (Locked Rotor Amps) | 6.0-7.5 A |
| Type of Relay | PTC Relay |
| COP | 1.25 W/W |
| Voltage Range | 187-254V |
| Max Condensing Temperature | 60°C (Continuous) / 70°C (Short) |
| Thermal Protection | Yes (Internal Thermal Protector) |
| Net Weight | 6.5-7.0 kg |
| Origin | Manufactured in China |
Efficiency Metrics (COP) Table
Performance varies based on operating conditions. Here is how the L65CZ1 performs across the temperature spectrum:
| Evaporating Temp (°C) | Cooling Capacity (Watts) | Power Consumption (Watts) | COP (W/W) |
|---|---|---|---|
| -25 | 135 | 130 | 1.04 |
| -20 | 165 | 140 | 1.18 |
| -15 | 200 | 150 | 1.33 |
| -10 | 240 | 160 | 1.50 |
| -5 | 285 | 170 | 1.68 |
| 0 | 335 | 180 | 1.86 |
| 5 | 390 | 190 | 2.05 |
| 10 | 450 | 200 | 2.25 |
Replacement Models
| Brand | Model Number |
|---|---|
| Donper | L65CZ1 |
| Donper | L65CZ variants |
5 Replacements (Same R134a Gas)
- Embraco NEK6196Z (Strong alternative, 1/5 HP, 6.5cc)
- Tecumseh THG1352YLS (Classic reliable swap, 1/6 HP)
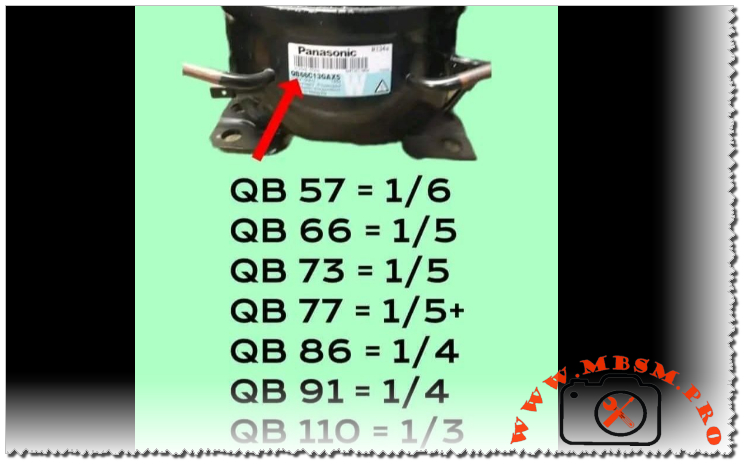
- Panasonic QB66C13GAX5 (Excellent domestic equivalent, 6.6cc)
- Cubigel GL80AA (Similar capacity, 7.8cc)
- Huayi HYE11YG (Budget-friendly alternative, 1/6 HP)
5 Replacements (Other Gas – R600a/R404A)
Note: Requires complete system flush and expansion valve/capillary adjustment.
- Embraco EGU80HLP (R600a – Isobutane, very efficient, 1/6 HP)
- Danfoss SC10CNX (R290 – Propane, high efficiency)
- Tecumseh CAJ9480Z (R404A – Higher capacity)
- Secop NL9FK (R600a compatible variant)
- Cubigel HM80AA (R600a – Energy efficient)
Key Features
- Thermally protected compressor
- Designed for Low Back Pressure (LBP) applications
- Suitable for domestic refrigerators up to 280L capacity
- RSIR motor type with PTC relay starting
- Evaporating temperature range: -25°C to +10°C
- Manufactured in China with RoHS compliance
- Energy efficient with COP of 1.25
- Low noise and vibration operation
- Wide voltage range compatibility (187-254V)
Focus Keyphrase: Donper L65CZ1 Compressor Specs and Replacements
SEO Title: Mbsm.pro – Donper L65CZ1 Compressor: 1/5 HP R134a Technical Guide
Meta Description: Looking for L65CZ1 specs? We break down this 1/5 HP R134a Donper compressor including cooling capacity (158-170W), wiring, oil type, and the top replacement models for domestic refrigeration.
Slug: donper-l65cz1-compressor-1-5-hp-r134a-specs
Tags: Mbsmgroup, Mbsm.pro, mbsmpro.com, mbsm, Donper, L65CZ1, R134a, 1/5 HP, LBP, Low Back Pressure, NEK6196Z, THG1352YLS, QB66C13GAX5, GL80AA, Compressor Replacement, HVAC, Refrigeration Repair, Domestic Refrigerator, China
Excerpt: The Donper L65CZ1 is a reliable 1/5 HP compressor designed for R134a LBP systems, commonly found in domestic refrigerators and freezers up to 280L capacity. This guide provides the full technical data sheet, including cooling capacity (158-170W at ASHRAE), oil requirements (280-320ml), and a comprehensive list of compatible replacements for both R134a and modern alternative refrigerants to ensure your repair is successful.