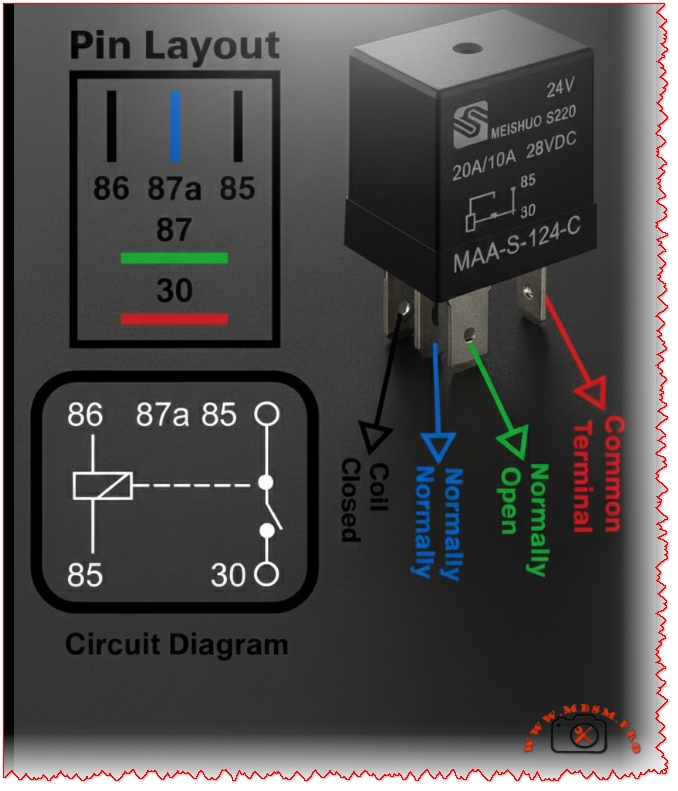
Relay, model MAA‑S‑124‑C, is a 24 VDC, 5‑pin

Mbsmpro.com, Relay, MEISHUO MAA‑S‑124‑C, 24V, 20A/10A, S220, 5‑Pin, DIN 72552, Terminals 30‑85‑86‑87‑87a, SPDT, Automotive, Coil, Normally Open, Normally Closed
Understanding the MEISHUO MAA‑S‑124‑C 5‑Pin Automotive Relay
The MEISHUO S220 series relay, model MAA‑S‑124‑C, is a 24 VDC, 5‑pin SPDT automotive relay rated 20 A/10 A at 28 VDC, widely used in vehicles and industrial control panels.
Its terminals follow the DIN 72552 standard numbering: 30, 85, 86, 87 and 87a, which simplifies wiring and troubleshooting for technicians.
Relay terminal functions (DIN 72552)
The DIN 72552 standard assigns each pin a clear functional role that does not depend on the physical layout of the housing.
This universal coding is crucial when replacing relays in mixed fleets, where the same harness may receive different brands or body styles.
Table 1 – Terminal numbers and roles
Internal SPDT changeover architecture
Internally, this relay is a single‑pole double‑throw (SPDT) changeover design: one moving armature switches the common terminal 30 between 87a (NC) and 87 (NO).
When no voltage is applied to 85–86, 30 remains connected to 87a; once the coil is powered, a magnetic field pulls the armature and transfers 30 to 87, never joining 87 and 87a at the same time.
Table 2 – Contact state vs coil status
Key electrical specifications and practical limits
While the S220 MAA‑S‑124‑C is rated at 20 A/10 A at 28 VDC, the NC path (30–87a) typically carries the lower current rating compared with the NO path (30–87), a common convention for changeover relays.
Coil voltage is fixed at 24 VDC, and coil resistance in similar MEISHUO 24 V changeover models is around 1.6 kΩ, giving a coil power of roughly 0.36 W, which helps in low‑power control systems.
Table 3 – Typical MEISHUO 24 V changeover relay data
*Values for generic industrial SSRs.
Comparison with standard ISO mini automotive relays
Standard ISO mini relays share the same numbering but often target 12 V passenger vehicles, whereas the MAA‑S‑124‑C addresses 24 V commercial, HVAC or industrial systems.
Type‑A and Type‑B ISO layouts may swap the physical locations of pins 30 and 86, but the numeric role stays constant, so technicians working with mixed stocks must always wire by number, not by drawing lines from the plastic footprint.
Table 4 – MEISHUO S220 vs generic ISO mini relay
Practical wiring scenarios for technicians
A 5‑pin SPDT relay like this offers flexible logic: the same control signal can switch loads that must be ON with the system and loads that must be OFF at the same time.
In an HVAC unit, for example, a 24 V thermostat output connected to 86 can feed the compressor contactor on 87, while 87a maintains a safety interlock loop when the compressor is idle.
Table 5 – Example wiring schemes using terminals 30‑85‑86‑87‑87a
Advantages over simple 4‑pin NO relays
Compared with a basic 4‑pin make‑and‑break relay, the 5‑pin MAA‑S‑124‑C supports changeover logic without extra components, saving wiring time and panel space.
Because 87a is closed at rest, designers can implement safety interlocks that drop out automatically once the relay energizes, improving fault detection in automotive and industrial controls.
Focus keyphrase (Yoast SEO)
MEISHUO MAA‑S‑124‑C 5‑pin relay 30‑85‑86‑87‑87a DIN 72552 terminal functions and wiring guide for 24V automotive and industrial control
SEO title (Yoast SEO)
MEISHUO MAA‑S‑124‑C Relay 24V, 5‑Pin 30‑85‑86‑87‑87a Wiring Guide | Mbsmpro.com
Meta description (Yoast SEO)
Learn how to wire the MEISHUO MAA‑S‑124‑C 24V 5‑pin relay using DIN 72552 terminals 30, 85, 86, 87 and 87a. See pin functions, tables, examples and comparisons for automotive and industrial control.
Slug (Yoast SEO)
meishuo-maa-s-124-c-5-pin-relay-30-85-86-87-87a-wiring
Tags
MEISHUO relay, MAA‑S‑124‑C, S220 relay, 5 pin relay, SPDT relay, DIN 72552, terminal 30 85 86 87 87a, automotive relay, 24V relay, relay wiring, relay pinout, HVAC control relay, industrial control relay, Mbsmgroup, Mbsm.pro, mbsmpro.com, mbsm
Excerpt (first 55 words)
The MEISHUO S220 series relay, model MAA‑S‑124‑C, is a 24‑volt 5‑pin SPDT automotive relay rated 20 A/10 A at 28 VDC. Its DIN 72552 terminal numbering—30, 85, 86, 87 and 87a—gives technicians a universal language for wiring and troubleshooting in vehicles, HVAC equipment and industrial control panels.

