Refrigerants, Standing, Suction and Discharge Pressures for Modern HVAC Systems
Guide to Common Refrigerants: Standing, Suction and Discharge Pressures for Modern HVAC Systems
Refrigeration technicians today work with a mix of legacy and new-generation refrigerants, each with its own safe pressure range and boiling temperature. Understanding these values is essential for accurate diagnostics, safe charging and long compressor life in air‑conditioning and commercial refrigeration.
Key role of pressure charts
Pressure–temperature charts and standing/suction/discharge tables give technicians a fast reference for what a system “should” be doing at a given ambient or evaporating temperature.
Using wrong reference values can lead to over‑charging, overheating, liquid slugging or misdiagnosis of a healthy system as faulty.
Overview of common refrigerants
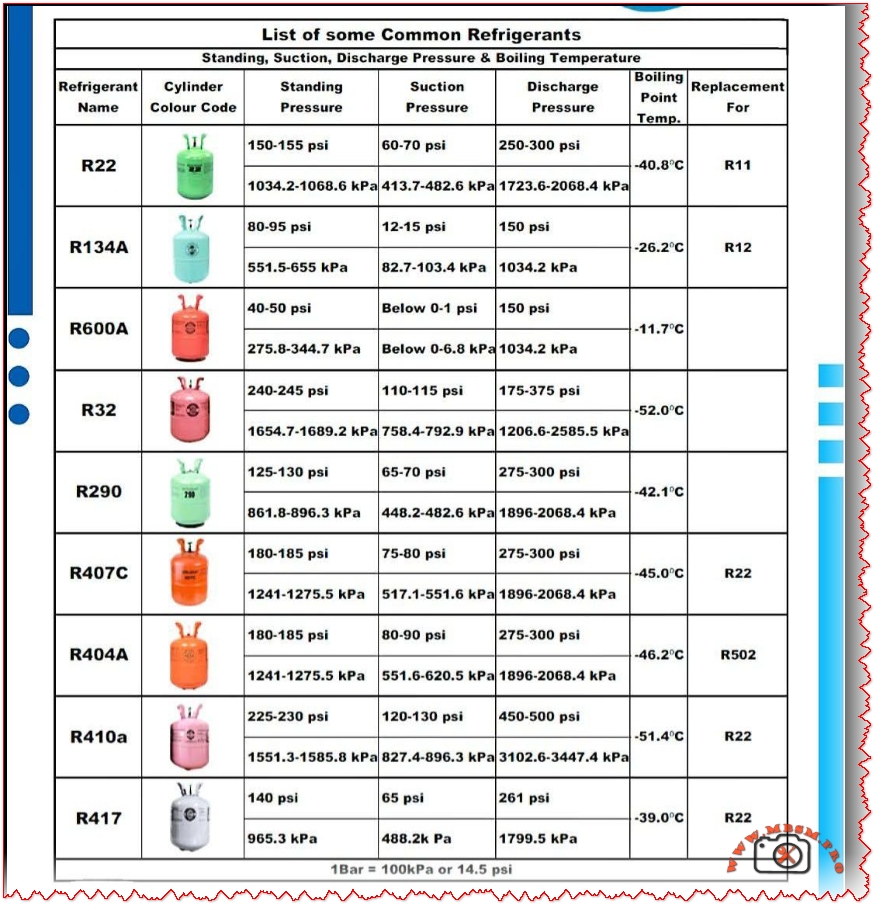
The image groups the most used refrigerants in residential and light commercial systems: R22, R134a, R600a, R32, R290, R407C, R404A, R410A and R417 (R417A).
Each gas has a typical standing pressure (static pressure at rest), an evaporating suction pressure, a condensing discharge pressure and a characteristic boiling point at atmospheric pressure.
Typical pressure ranges from the chart
The following table summarises the indicative values shown in the chart (all pressures are approximate, for normally loaded systems at typical comfort‑cooling conditions).
Indicative pressures and boiling points
These figures are not universal “set‑points”, but practical targets that help technicians decide whether a system is under‑charged, over‑charged or suffering airflow or mechanical problems.
Safety, cylinder colours and replacements
Many countries use conventional cylinder colour codes to identify refrigerants quickly on site, although some regions are migrating to neutral colours with clear labelling.
Hydrocarbons such as R290 and R600a are flammable, so working pressures must always be combined with strict leak‑prevention, ventilation and ignition‑control procedures.
When phasing out ozone‑depleting R22, blends like R407C or R417A are often used in retrofit projects, while new high‑efficiency equipment typically relies on R410A or R32 with different design pressures.
Comparing the standing and operating pressures during commissioning helps ensure that a replacement refrigerant is compatible with existing components such as compressors, valves and heat‑exchangers.
Practical use for technicians and trainers
- Technicians can laminate similar tables and keep them in the toolbox or on the workshop wall as a quick‑reference during charging and troubleshooting.
- Training centres and HVAC content creators like Mbsmgroup and Mbsm.pro can turn these values into interactive quizzes, infographics or mobile‑friendly charts for students and new technicians.